Machine Library Tutorial
Contents
Introduction
This tutorial will step through the process of adding two different machines (Rotary draw and rotary compression) to the machine library using the machine library plug-in.
The machine library plug-in is used to create different machines by assigning specific settings to them. These settings include the way rotations and lengths/locations are measured, the decimal tolerances for lengths, angles, and rotations, and default cut offs. Machines are selected during the part design process and all the machine's settings will be applied to the part.
Tutorial Pt.1: Rotary Draw Machine
Step 1
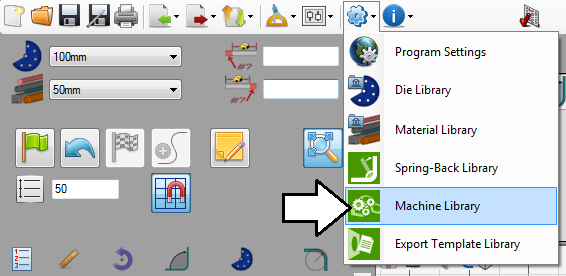
First, open the machine library. Go up to the main menu bar and click on the settings menu. Select the machine library option from the drop down menu.
Step 2
This will open the machine library. A list of the machines will be shown to the right. To the left, there will be a tabbed section where the machine settings will be chosen.
Step 3
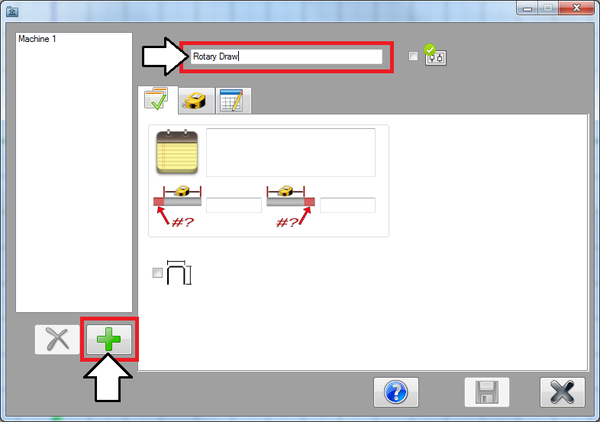
Now the first machine will be created. Click the add button. Enter the machine's name, "Rotary Draw", in the field above the tabs near the top of the window.
Step 4
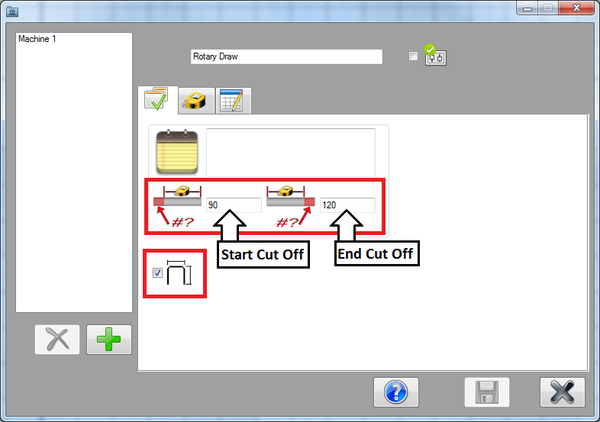
In the first tab, the default settings can be chosen.
In the start cut off field, enter 90. In the end cut off field, enter 120.
Check the box next to the display dimensions icon. When checked, the part model in the part designer will include the dimension markers and values.
Step 5
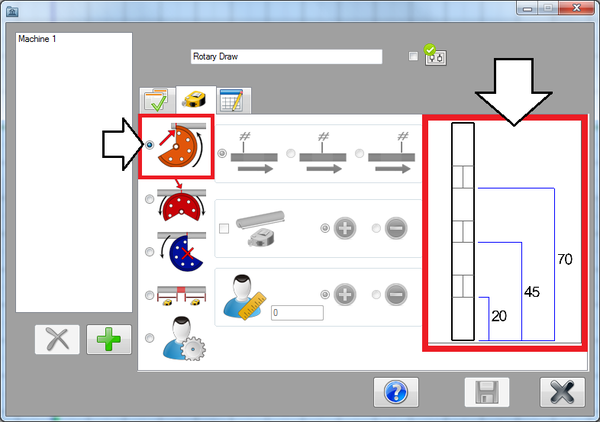
Next, click on the second tab. In this tab, the format of the results table can be chosen.
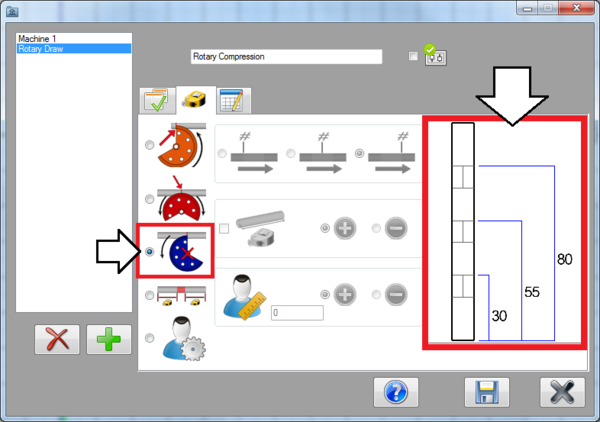
Since this machine is going to be a rotary draw machine, select the pre-defined rotary draw option.
Dimensions will start at the beginning of the part and end at the start of each bend. An example of how the dimensions will be placed are shown to the right of the format selection area.
Step 6
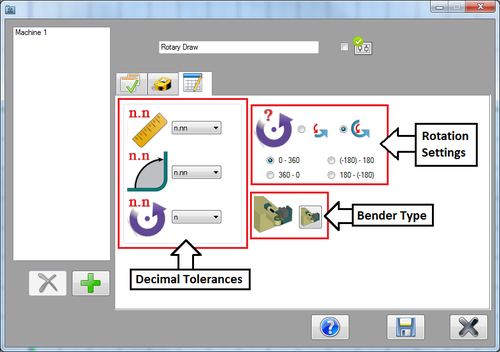
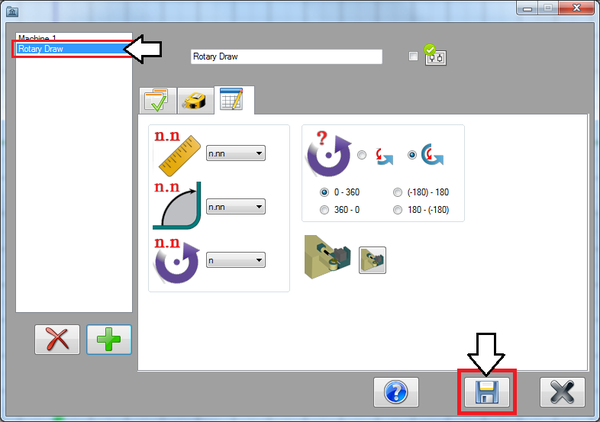
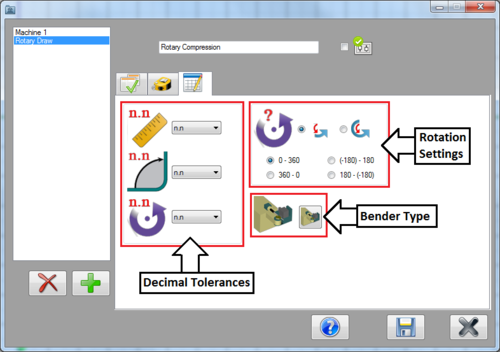
Now click on the third tab. This is where the decimal tolerances, rotation settings, and bender type can be set.
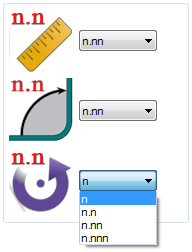
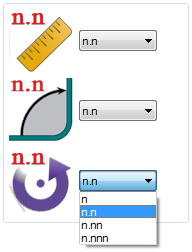
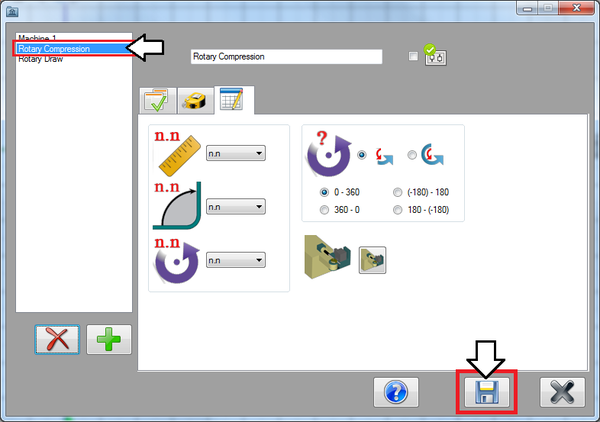
The decimal tolerances control how many digits are allowed after decimal points for length, angle, and rotation values. Select the 'n.nn' option for both length and angle. Lengths and angles will be allowed two decimal places. For rotation, select 'n'. Rotations will only be whole numbers. See the image below.
The rotation settings control how rotations are interpreted and displayed in the results table. Select the Absolute rotation option. For the rotation scale, select the '0 - 360' option. Absolute rotation means that the rotations will be measured from the beginning of the scale at each new rotation. The scale determines where the rotation angles start and end. See image below.
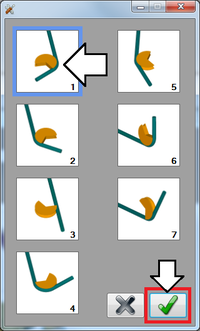
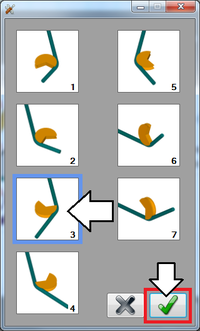
Lastly, the bender type will be chosen. Click the bend type button to open the bender type menu. Click on the first bend type (rotary draw) to select it. Click the green check button to confirm, as shown in the image below.
Step 7
Now that all the settings are applied to the machine, click the save button. The machine will be added to the machine list on the left.
Tutorial Pt.2: Rotary Compression Machine
Step 8
Now, the next machine will be added to the library.
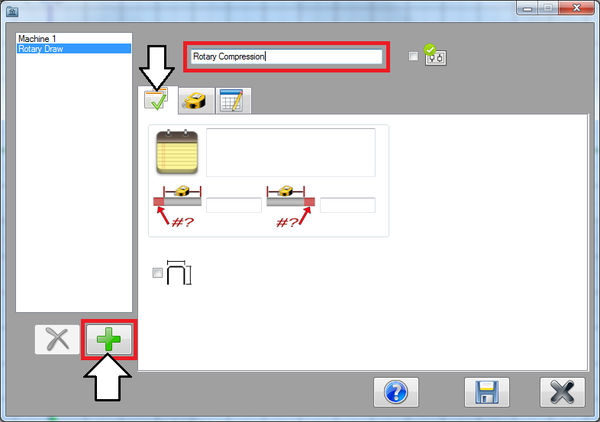
Click the first tab. Then click the add button again. Enter "Rotary Compression" in the name field.
Step 9
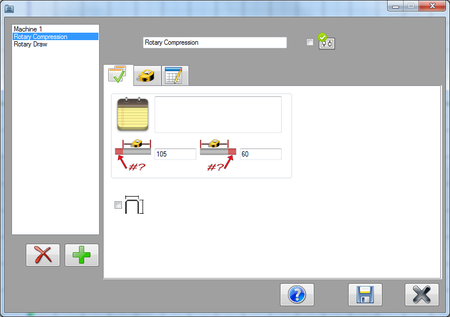
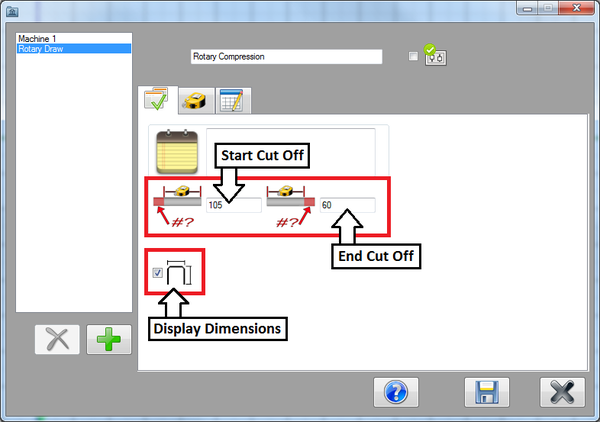
Next, the default cut off lengths will be set. Enter 105 into the start cut off field and enter 60 into the end cut off field.
Then check the box next to the display dimensions icon.
Step 10
Next, click on the second tab.
Since this machine will be a rotary compression machine, select the pre-defined rotary compression option.
The dimensions will start at the beginning of the part and end at the end of each bend. An example of how the dimensions will be placed are shown to the right of the format selection area.
Step 11
Next, click on the third tab. This is where the decimal tolerances, rotation settings, and bender type can be set.
The decimal tolerances control how many digits are allowed after decimal points for length, angle, and rotation values. For length, angle, and rotation, select the 'n.n' option.
The rotation settings control how rotations are interpreted and displayed in the results table. Select the Incremental rotation option. Incremental rotation means each new rotation will start at the end of the last rotation. For the rotation scale, select the '0 - 360' option.
Lastly, the bender type will be chosen. Click the bend type button to open the bender type menu. Click on the third bend type (rotary compression) to select it. Click the green check button to confirm, as shown in the image below.
Step 12
All the settings have been defined for this machine. Click the save button to save the machine and add it to the machine list to the left.
Then close the machine library by clicking the close button in the bottom right corner.
Tutorial Pt.3: Using Machines
Step 13
The next steps will require a complete part design. The part shown in these steps is the part created in the Linear 2D Designer Tutorial. Either complete Linear 2D Designer Tutorial or create a new part from scratch before proceeding.
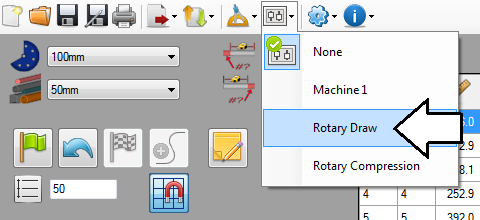
First, the rotary draw machine will be applied to the part. Go up to the main menu bar and click the machine menu. Select the Rotary Draw machine from the drop down menu.
Step 14
The rotary draw machine settings will now be applied to the part.
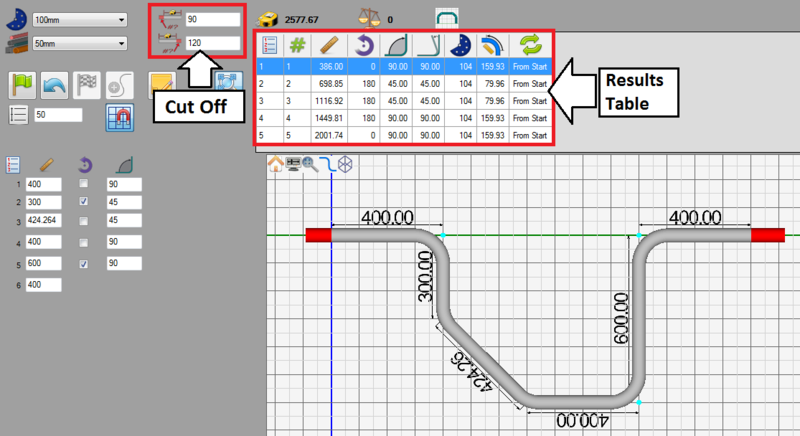
The cut off values (supplied in step 4) from the machine will be generated in the cut off fields to the left of the results chart.
In the results chart, there will be three major changes:
1.) The decimal tolerances (chosen in step 6) were applied to the length, angle, and rotation values. Lengths and angles are allowed 2 decimal places and rotations are only whole numbers.
2.) The length/locations will be measured differently due to the rotary draw results format chosen in step 5.
3.) The rotations will be measured in absolute terms (from step 6).
Step 15
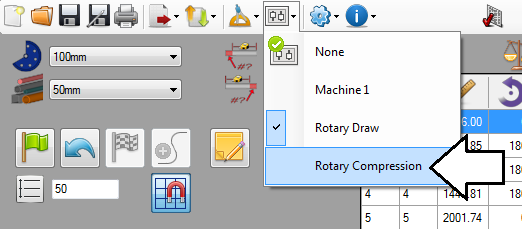
Next, the rotary compression machine will be applied to the part. Go up to the main menu bar and click the machine menu. Select the Rotary Compression machine from the drop down menu.
Step 16
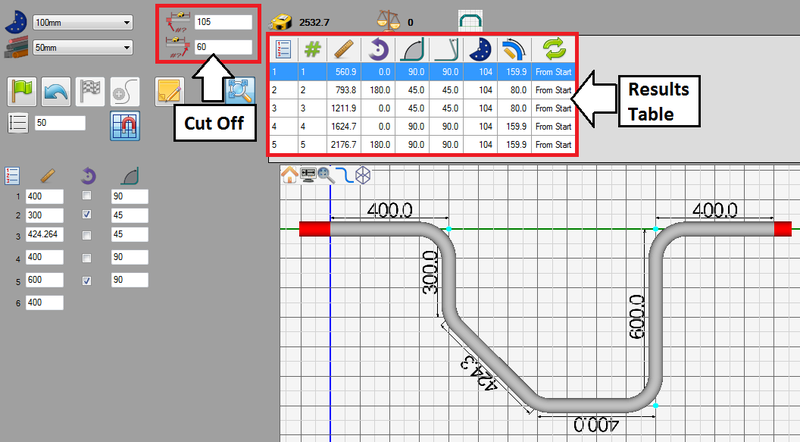
The rotary compression machine settings will now be applied to the part.
The cut off values (supplied in step 9) from the machine will be generated in the cut off fields to the left of the results chart.
In the results chart, there will be three major changes:
1.) The decimal tolerances (chosen in step 11) were applied to the length, angle, and rotation values. Lengths, rotations, and angles will only be allowed one decimal place.
2.) The length/locations will be measured differently due to the rotary compression results format chosen in step 10.
3.) The rotations will be measured incrementally (from step 11).